TB and HIV are overlapping epidemics, both have been declared global emergencies demanding global attention. There is an increasing recognition of the need to strengthen collaboration between national TB and HIV/AIDS programmes and other stakeholders in countries around the world because of the overlapping nature of TB and HIV infection. In particular, there is evidence that HIV infection weakens the immune system, thereby fuelling the TB epidemic among people living with HIV/AIDS (PLHA).
Tanzania Ministry of health developed National Policy Guidelines for Collaborative TB/HIV activities with the overall objective to provide a framework for ensuring transparent and consistent processes in developing comprehensive collaborative TB/HIV activities. This objective emphasizes the need for joint decision-making processes that take into account the comparative advantages of the NTLP, NACP, and other stakeholders.
TB/HIV CASE FINDING 2021
A total of 85,749 (99%) of the 86,653 new and relapse TB cases notified in 2021 were counselled and tested for HIV status. This is below the 2020 result and End TB plan targets of 100. Of those tested, 15,287 (18%) were found to be co-infected with HIV which was lower than the co-infection rate in 2020 of 21%. Among the co-infected cases in 2021, 15,189 (99%) cases were initiated or continued on ART in both TB and CTCs within the three months reporting period after a two weeks tolerance period after starting TB treatment. Figure 10 and 11 below summarizes TB/HIV services in the country in 2021.
Figure 18: Percentage of co-infection among TB cases by region in 2021

Figure 19 Co-infection rate among age group of new and relapse TB cases notified 2021

Figure 20: HIV positive TB cases initiated or continuing with ART during TB treatment

Childhood TB/HIV case notifications 2021
Figure 21, shows the co-infection of HIV and TB among children notified with TB in 2021. Testing and counseling for HIV is also done to children (under the age of 15) attending the TB clinics. In 2021 data shows 1,264 (9%) were HIV co-infected cases, with age group 10 – 14 more infected than the younger age groups. Among all co-infected cases notified in 2014, children make up 8.3% of all cases.
TPT provision to Children
Children under 5 years of age who are exposed to bacteriologically Confirmed TB patients are normally screened for TB and those found with no presumptive TB are initiated TB Preventive Therapy. For the presumptive TB cases, active TB disease is rolled out according to the national guidelines. The percent of under 5 children eligible for TPT has increased from 6.3% in 2016 to 82.4% in 2023. The missing data in 2015 was due to incomplete reporting as DHIS2 ETL was not existing. Moreover in 2023, the country has surpassed the set target of 80%.
Trends of proportion of children household contacts of bacteriologically confirmed pulmonary TB cases initiated TPT
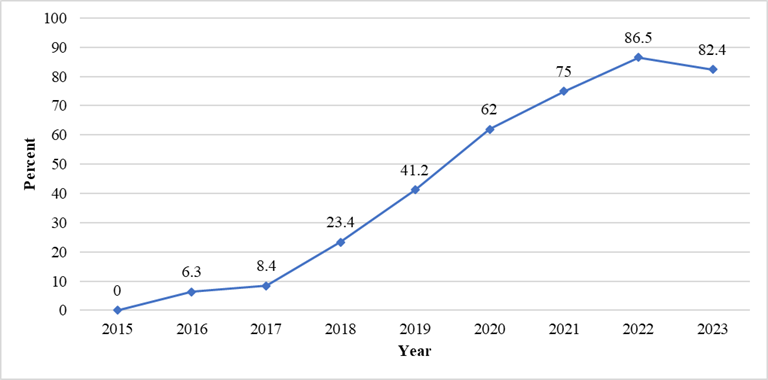
Figure 21: Trend of proportion of Children under 5 years of age household contacts of bacteriologically confirmed Pulmonary TB cases initiated on TPT
Proportion of children household contacts of bacteriologically confirmed Pulmonary TB cases initiated TPT in 2023 by region
As shown in the figure 22 below, 15 regions had low proportion of children <5years who started on TPT as compared to the set national target of 80%. The top five TB and Leprosy regions with high proportion are Tabora (143), Simiyu (121.6), Geita (113.8), Kilimanjaro (113.7) and Dodoma (107.1). Low proportion was observed in Lindi (33.9), Pwani (34.5), Mwanza (36.6), Ilala ii (41.7) and Iringa (42.5).
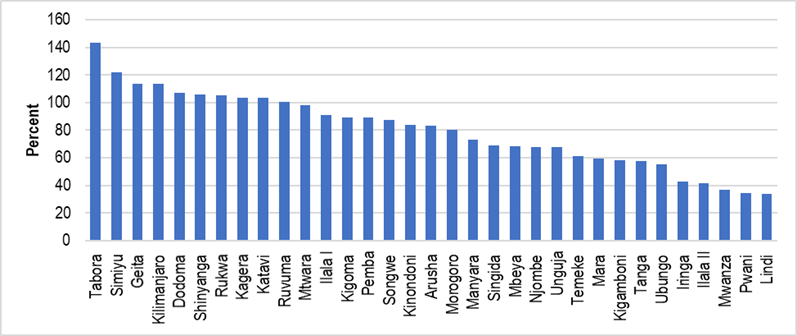
Figure 22: Percentage of children (aged < 5 years) household contacts of bacteriologically-confirmed TB cases who started TPT by regions, (Source: DHIS2-ETL)